EV Fuse and Selection Guide
SOC’s compact and high-performance fuses for an EV originated from the fuses for the world’s first mass-produced EV.
Extensive experience in the protection of a car battery, high-voltage circuit, on-board charger, and auxiliary equipment.
There are also products not listed on the web. Our experienced engineers are ready to assist you
with fuse selection, testing, new products, customization, etc.
EV Fuse Selection Guide
This guide provides information on how to select the appropriate fuses for EV
(BEV/HEV/PHEV/FCV) application. If you have any questions about fuses, please feel free
to contact us.
What is needed for EV fuses?
Fuses are important safety devices that protect us from short circuits or abnormal currents
that can cause smoke, fire, or damage. The circumstances around EV fuses involve hectic
heat/humidity fluctuations and strong vibrations, which would not occur in other electrical
appliances. EV fuses must have high reliability under such extremely harsh conditions for a
long period of time, and must be capable of successfully interrupting high voltage current in
the circuit.


What fuses are needed for each circuit?
There are different types of circuits in an EV. Choosing the appropriate fuses depends on
each circuit’s requirements.
 The main circuit has large current fluctuations even during normal use. The fuse for the
main circuit must withstand this large current. This is particularly the case for EVs as fast
charging is required to fill the battery to enable long-distance driving on a single charge. It
must also quickly interrupt accidental fault current to prevent any smoke and fire of
relays/wire, or damage caused by semiconductor breakage.
The main circuit has large current fluctuations even during normal use. The fuse for the
main circuit must withstand this large current. This is particularly the case for EVs as fast
charging is required to fill the battery to enable long-distance driving on a single charge. It
must also quickly interrupt accidental fault current to prevent any smoke and fire of
relays/wire, or damage caused by semiconductor breakage.
 In the DC-DC converter circuit, fuses are required to have the protection coordination with
other overcurrent protection functions. At the same time, it must quickly operate to prevent
the accidental fault current caused by the malfunction of the semiconductor switch from
spreading to the other circuit. The downsizing of fuse is also an important factor due to the
high density of circuit board.
In the DC-DC converter circuit, fuses are required to have the protection coordination with
other overcurrent protection functions. At the same time, it must quickly operate to prevent
the accidental fault current caused by the malfunction of the semiconductor switch from
spreading to the other circuit. The downsizing of fuse is also an important factor due to the
high density of circuit board.
Main circuit
 The main circuit has large current fluctuations even during normal use. The fuse for the
main circuit must withstand this large current. This is particularly the case for EVs as fast
charging is required to fill the battery to enable long-distance driving on a single charge. It
must also quickly interrupt accidental fault current to prevent any smoke and fire of
relays/wire, or damage caused by semiconductor breakage.
The main circuit has large current fluctuations even during normal use. The fuse for the
main circuit must withstand this large current. This is particularly the case for EVs as fast
charging is required to fill the battery to enable long-distance driving on a single charge. It
must also quickly interrupt accidental fault current to prevent any smoke and fire of
relays/wire, or damage caused by semiconductor breakage.
On-board charger circuit
The on-board charger circuit requires AC rated fuses on the input side where power is
supplied and DC rated fuses on the output side where power is output from the charger.
The AC rated fuse must satisfy the following requirements: protection coordination with
relays on the power supply side, sufficient breaking capacity estimated by the impedance of
the power supply circuit, and compliance with required standards or regulations. The DC
rated fuse must interrupt an accidental current quickly so as not to affect the upper circuit.
In addition, the size and weight of both AC and DC rated fuses are expected to be reduced
according to the downsizing of on-board chargers.


DC-DC converter circuit
 In the DC-DC converter circuit, fuses are required to have the protection coordination with
other overcurrent protection functions. At the same time, it must quickly operate to prevent
the accidental fault current caused by the malfunction of the semiconductor switch from
spreading to the other circuit. The downsizing of fuse is also an important factor due to the
high density of circuit board.
In the DC-DC converter circuit, fuses are required to have the protection coordination with
other overcurrent protection functions. At the same time, it must quickly operate to prevent
the accidental fault current caused by the malfunction of the semiconductor switch from
spreading to the other circuit. The downsizing of fuse is also an important factor due to the
high density of circuit board.
Auxiliary application circuit
In the circuit for numerous auxiliary applications such as heater, air conditioner and ECU,
various requirements are assumed. The fuses for this circuit must withstand the maximum
current at normal use without melting, and quickly interrupt the accidental fault current not
to affect the upper circuit.
Desired characteristics of EV fuses
The following characteristics should be considered when selecting EV fuses.


Rated current
The fuse must be able to withstand rush current or transient current during normal usage,
and must prevent the circuit devices from smoke or fire caused by abnormal current.
Therefore, the rated current of the fuse is evaluated in reference with the I-t /I2t-t and
temperature re-rating curves. To avoid nuisance fusing, a sufficient margin should be
considered, which differs depending on fuse types or fuse manufactures.
Rated voltage
The voltage of EV batteries has increased in order to reduce power loss and charging time.
The higher voltage tends to prolong the arc current, which can increase the risk of damaging
the fuse itself. The maximum voltage that the fuse can safely interrupt should be considered
together with the rated breaking current. The rated voltage must be larger than the circuit
voltage.
Rated breaking current
In response to the growing need for greater EV power, the output current of EV batteries
tends to become larger, and the short-circuit current at accident also becomes larger. The
rated breaking current represents the maximum current the fuse can successfully interrupt
when an accidental fault current occurs. The rated breaking current should be larger than
the short-circuit current taking into account the relevant regulations or circuit impedance.


Size and shape
Since the size of fuse is closely related to the rated voltage or interrupting capacity, it is
important to select an appropriately sized fuse. Large current flows may generate heat due
to the contact resistance at the junction, therefore, we recommend bolted-connection-type
fuses to ensure solid mounting.



Ambient temperature
Fuses are affected by ambient temperature. The inside of an EV has a relatively higher
temperature compared to other electrical appliances. The ambient temperature should be
within the range recommended by the fuse manufacturer. This may require careful review of
the margin or rated current.
Pre-arcing time-current characteristic (I-t curve)
The I-t curve of a fuse is used to select a fuse which will successfully operate under the given
conditions of the short circuit withstand of relays or the fuming characteristics of wire. In
the high-voltage EV circuit, the fuse element will melt to interrupt the small accidental
current as indicated in the relevant I-t curve. However, there is a possibility of the arc
current continuing if the melted part of the element is too narrow to interrupt the current.
Therefore, the minimum breaking current should also be considered.
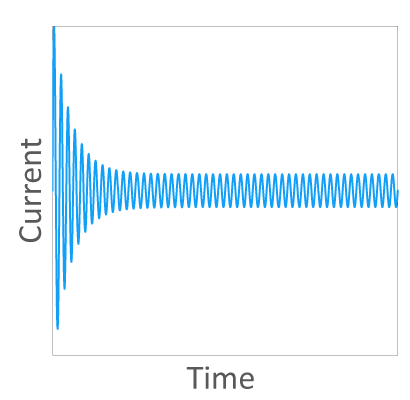
Fuse Selection Based on Current Waveform
The conventional current waveform, which consists of the inrush current at power-on and
the constant current at normal use, can be used to select an appropriate fuse in reference
with the conventional I2t-t curve and I-t curve. However, the current waveform in the EV
circuit is usually complex and may not always be properly evaluated by I2t-t curves readily
available. This evaluation requires extensive work. SOC can assist with selecting appropriate
fuses for each customer’s application. Please feel free to contact us.
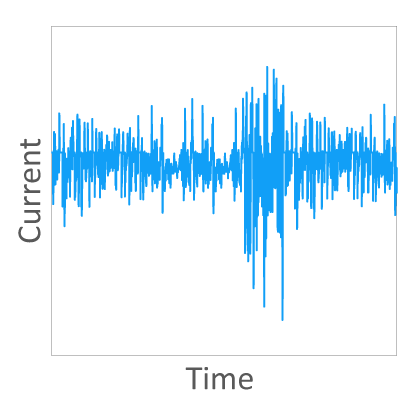
Protection Coordination with EV Relay
EV relays are used to open and close high voltage circuit. To prevent secondary damages
caused by the burning of the relay contact, the evaluation of the protection coordination
matching between fuse and relay will be critical.
SOC can provide a matching test for EV relays and fuses. Please do not hesitate to contact
us. (more information is available in our Technical Paper: How We Test Our Fuses).


AEC-Q200 Qualified Fuses
The Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) is an organization established in the 1990s by the
three major U.S. automakers and other major electronic component manufacturers.
It has developed and introduced common qualification specifications for in-vehicle components
exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Originally, fuses were not included in the AEC
specifications, but in 2023, the reliability test scope of AEC-Q200 for passive components was
updated by Revision E to include fuses. In response to this, SOC has been conducting tests for
a series of automotive fuses to make them AEC-Q200 qualified. The test mode varies
depending on the types of fuses. The following is an example of the test for a board-mounted
fuse (500VBI1030):
| No. | Test Item | Remark(s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pre- and Post- Stress Electrical Test | Fuse resistance is measured before and after each stress test. Overload operation and current-carrying capacity tests are conducted after each stress test. |
| 2 | High Temperature Exposure | 125℃ for 1000 hours |
| 3 | Temperature Cycling | -40℃ to 125℃ for 1000 cycles |
| 4 | Humidity Bias | 85℃ and 85% humidity for 1000 hours, with current energized at 10% of the rated current |
| 5 | High Temperature Operating Life | 125℃ for 1000 hours, with current energized considering derating |
| 6 | External Visual | Inspect the appearance of the fuse using a magnifying glass or similar tools |
| 7 | Physical Dimensions | Measure the external dimensions of the fuse |
| 8 | Resistance to Solvents | Immersion in prescribed solvent and brushing |
| 9 | Mechanical Shock | Sine half-wave at 100G-6ms |
| 10 | Vibration | Acceleration of 5G, frequency from 10-2000Hz, sweep rate of 20 minutes per cycle, for a total of 12 cycles |
| 11 | Resistance to Soldering Heat | Fuse is immersed in molten solder (solder temperature 260±5℃, maintained for 10±1 s) |
| 12 | Solderability | Inspect the wettability of the solder after immersing the terminals of the fuse in molten solder |
| 13 | Electrical Characterization | Temperature rise ≦ 150K at 1.0IN Current carrying capacity at 1.0IN Pre-arcing time ≦ 120s at 2.0IN Interruption test DC500V 2,000A with a resistance circuit |
| 14 | Board Flex | Mount a fuse on the test board and apply bending force to the board (bending depth 2mm, maintained for 60s) |
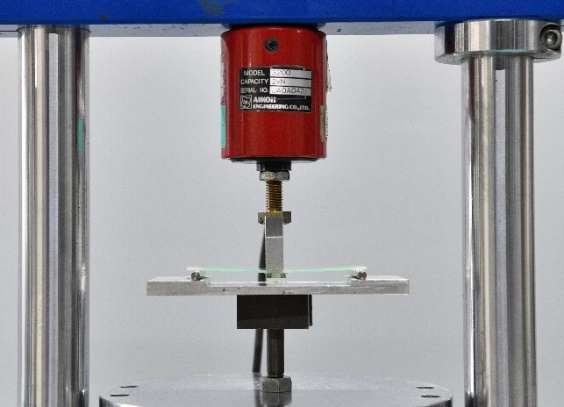
High Temperature Exposure Test

Board Flex Test
SOC’s Fuses for EVs
SOC manufactures various EV (BEV/HEV/PHEV/FCV) fuses. For example, the PT series,
which is designed for main circuit, has large rated voltage and rated current, excellent pre-
arcing characteristics, and high durability to protect EV circuit (more information available
in our Application Note: PT Series). We have other EV fuses which are not shown on our
website, so please feel free to ask us.
Conclusion
Selecting appropriate EV fuses for each application is critical for the safety and reliability of
the system. This guide provides some key points useful in choosing fuses, and we strongly
recommend contacting us on specific points that interest you. SOC has highly experienced
engineers who are more than happy to explain how to select the best fuse for your circuit.
We also provide fuse seminars tailor-made for our customers.
Please feel free to contact us by phone or e-mail.